No Biomass Monitoring
- Forces researchers to accept under-sampled experiments and "black box" shake flasks with limited bioprocess understanding
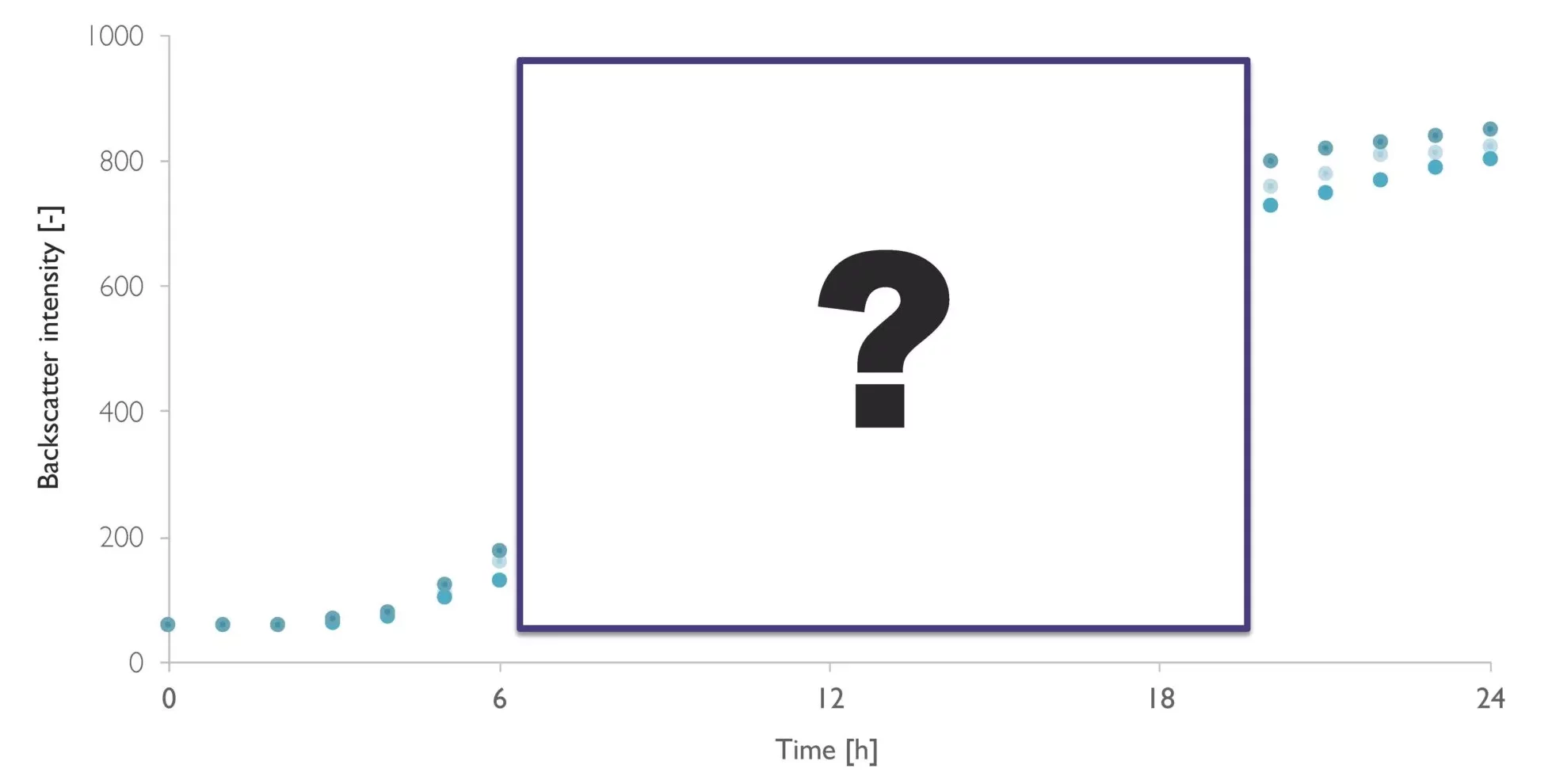
Monitor biomass and growth rates in your shake flask bioprocess with high resolution using the CGQ. Optical biomass measurements are based on backscattered light detection without the use of integrated sensors. Simply install the sensor plate under the shake flask and monitor the biomass through the vessel floor. Follow the growth of your cultures in real-time to gain actionable insights into your strain’s growth behavior.
Key Features
Benefits
Our Cell Growth Quantifier (CGQ) enables biomass monitoring in shake flasks. The CGQ’s technique for non-invasive cell density monitoring is based on the principle of light backscattering.
Using LEDs and photodiodes, the CGQ sensor emits light through the shake flask wall and measures the amount of light that is scattered back. The more cells that are in the medium, the more light is scattered back. This backscattered signal can be correlated with offline cell density data, such as OD600 or cell dry weight.
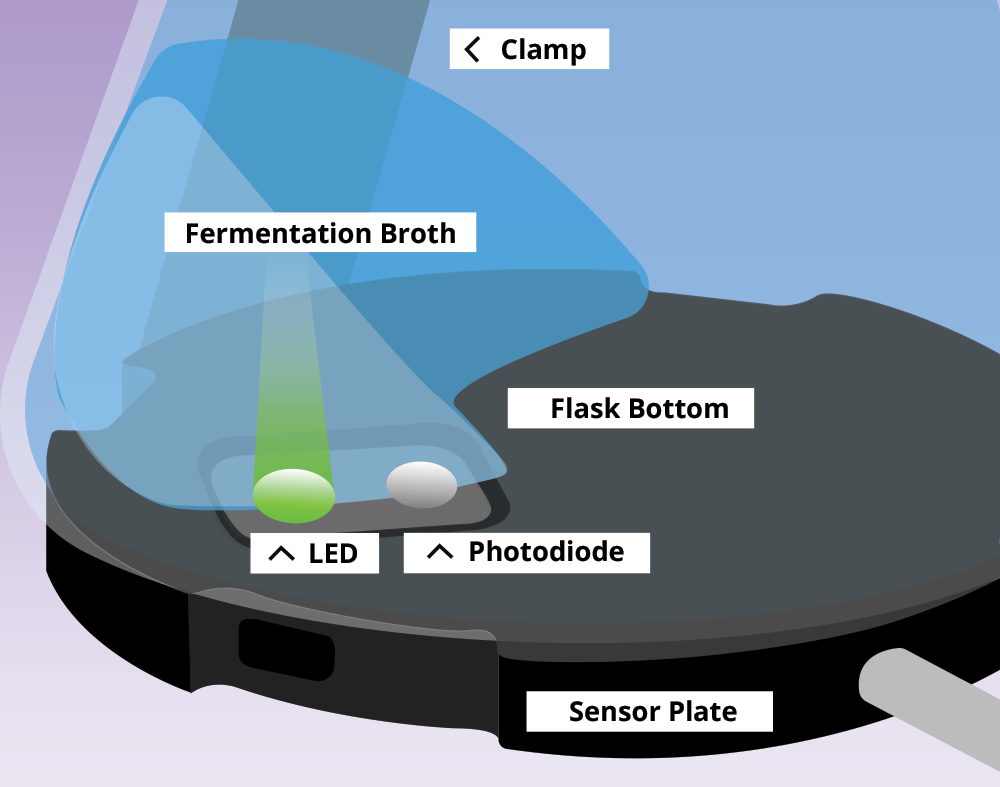
The sensor plate of the CGQ contains an LED light source and a photodiode detector. The CGQ’s innovative measuring method treats the signal fluctuations from the moving bulk liquid due to shaking as a valuable information source rather than noise.
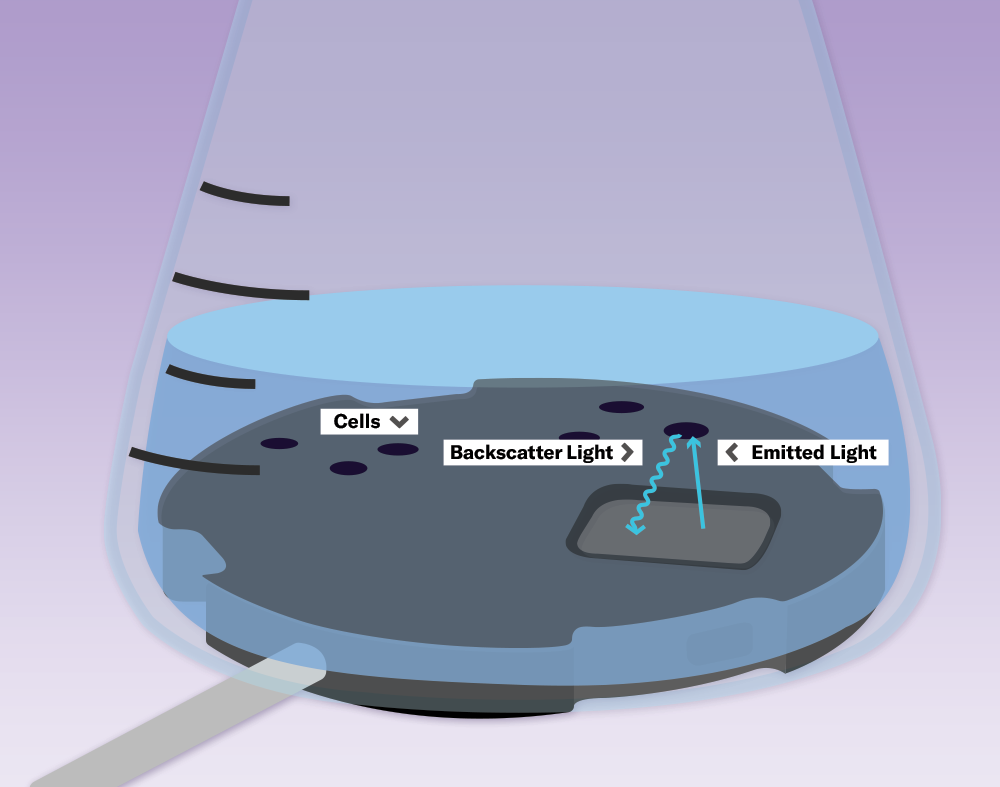
Light is emitted from the LED into the culture medium. While most photons go straight through the broth, some are scattered by the cells and return to the photodiode, which measures the scattered light intensity. The higher the cell density, the more light is scattered back to the photodiode.
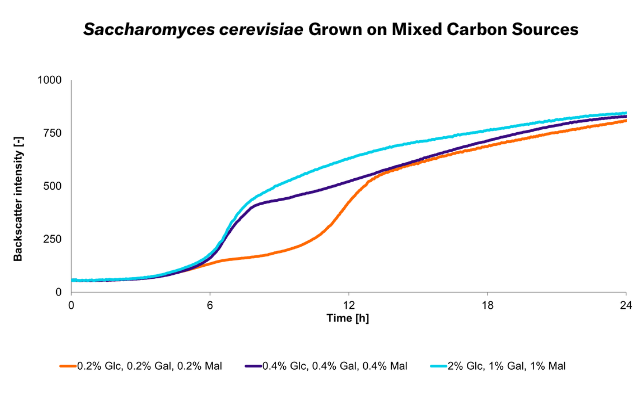
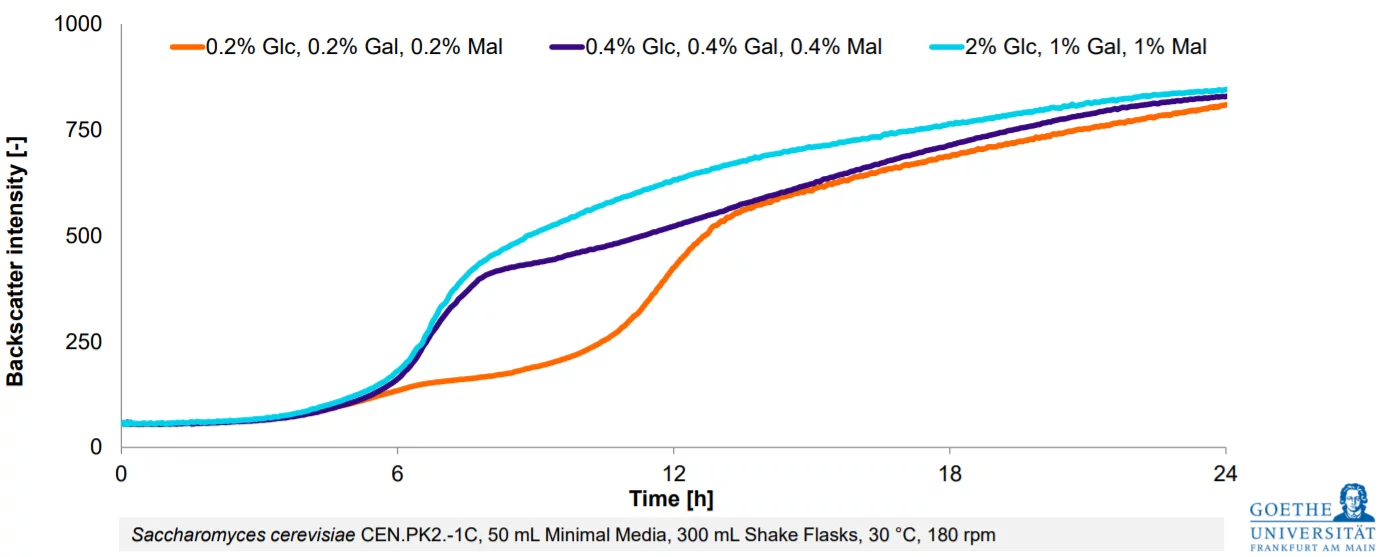
Saccharomyces cerevisiae CEN.PK2.-1C, 50 mL Minimal Media, 300 mL Shake Flasks, 30 °C, 180 rpm
The CGQ is ideal for screening experiments in shake flasks such as media optimizations. Shake flask fermentations can be automatically monitored regarding biomass and growth rates with high resolution and parallelization, making the CGQ a valuable tool for growth-based strain characterization and development.
The Cell Growth Quantifier (CGQ) aids in growth characterization experiments. Here, the growth media in shake flask cultivations of S. pasteurii were evaluated by monitoring the backscatter and oxygen transfer rate (OTR) during shake flask cultivation. The growth curves indicated a oxygen limitation.
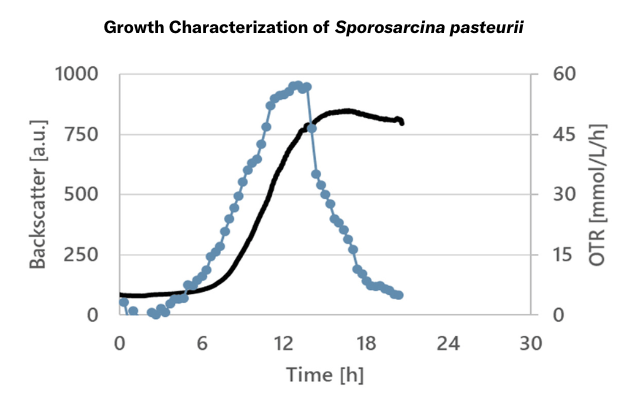
Sporosarcina pasteurii, 250 mL Shake Flasks, 10 mL Filling Volume, 50 mm Throw, 30 °C, 300 rpm
.png?width=800&height=500&name=Promotor%20Induction%20in%20Pichia%20pastoris%20with%20Biomass-based%20feeding%20(1).png)
Pichia pastoris (P. pastoris), 200 rpm/25 mm, 10 % filling volume, 250 ml flask, 37°C
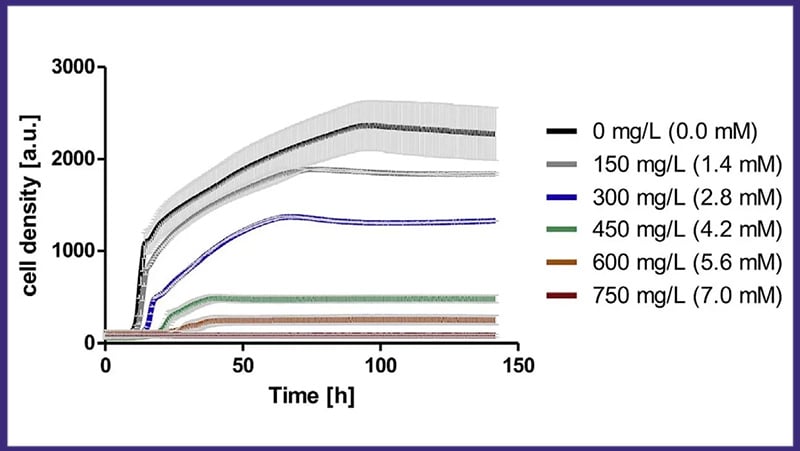
Biomass-based feeding in shake flasks uses the interconnectivity of sensors (CGQ) and actuators (Liquid Injection System) within the new DOTS Software to enable feedback controlled feeding in your shake flask experiments. The implementation of smart feeding strategies based on biomass measurements can help optimize your bioprocess.
In the described studies by Ingo Bauer et al., several growth experiments were conducted with the CGQ, testing different filamentous A. fumigatus wild type strains, mutants with previously reported growth defects, and different media compositions, imposing e.g., iron or nitrogen limitations. The results showed that the data produced with the CGQ was reliable and reproducible. Learn More →
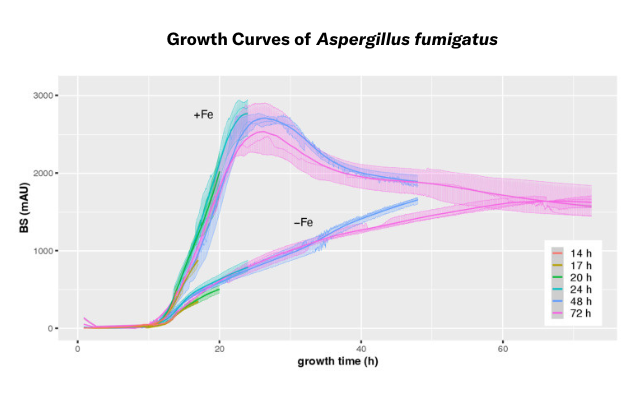
CGQ-mediated growth monitoring of A. fumigatus during 14–72 h liquid shake culturing under +Fe and −Fe conditions
Each sensor plate is positioned under the cultivation vessel and measures the biomass non-invasively through the vessel wall.
Several sensor plates can be connected to a single hub. The CGQ hub bundles the data from all monitored flasks and sends it to the DOTS Software.
The DOTS Software receives the data from the hub and visualizes backscattered light intensities in real-time, providing high-resolution growth curves.


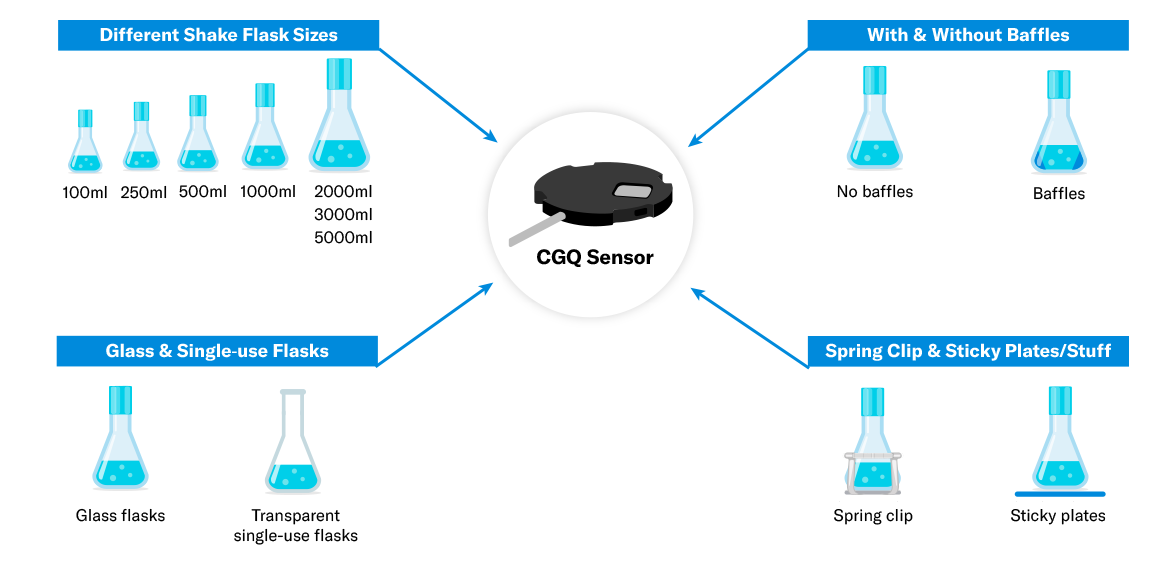
The CGQ is compatible with a variety of vessel types. An available adapter system provides maximum flexibility, allowing the same sensor plate to be used with different shake flask sizes.
Any shake flask size ranging from 100 mL to 5000 mL
Flasks with or without baffles
Glass and single-use flasks
Spring clip and Sticky Mat mounts
Example Organisms Successfully Monitored with CGQ Technology
Escherichia coli
Corynebacterium glutamicum
Bacillus subtilis
Pseudomonas putida
Pseudomonas taiwanensis
Gluconobacter oxydans
Lactobacillus plantarum
Vibrio natriegens
Vibrio cholerae
Staphylococcus aureus
Klebsiella pneumoniae
Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae
Chromobacterium violaceum
Blautia producta
Hungtatella hathewayi
Prevotella copri
Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Schizosaccharomyces pombe
Pichia pastoris
Yarrowia lipolytica
Kluyveromyces lactis
Hansenula polymorpha
Ustilago maydis
Aspergillus fumigatus
Aspergillus nidulans
Aspergillus niger
Streptomyces acidiscabies
Streptomyces venezuelae
Trichoderma reesei
Haloferax volcanii
Sulfolobus acidocaldarius
Acetobacterium woodii
Clostridium aectobutylicum
Clostridium ljungdahlii
Clostridium difficile
Chlorella vulgaris
Scenedesmus obliquus
Synechococcus elongatus
Nicotiana tabacum BY-2 (plant cells)

The CGQ is compatible with a variety of vessel types. An available adapter system provides maximum flexibility, allowing the same sensor plate to be used with different shake flask sizes.
Any shake flask size ranging from 100 mL to 5000 mL
Flasks with or without baffles
Glass and single-use flasks
Spring clip and Sticky Mat mounts
Example Organisms Successfully Monitored with CGQ Technology
Escherichia coli
Corynebacterium glutamicum
Bacillus subtilis
Pseudomonas putida
Pseudomonas taiwanensis
Gluconobacter oxydans
Lactobacillus plantarum
Vibrio natriegens
Vibrio cholerae
Staphylococcus aureus
Klebsiella pneumoniae
Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae
Chromobacterium violaceum
Blautia producta
Hungtatella hathewayi
Prevotella copri
Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Schizosaccharomyces pombe
Pichia pastoris
Yarrowia lipolytica
Kluyveromyces lactis
Hansenula polymorpha
Ustilago maydis
Aspergillus fumigatus
Aspergillus nidulans
Aspergillus niger
Streptomyces acidiscabies
Streptomyces venezuelae
Trichoderma reesei
Haloferax volcanii
Sulfolobus acidocaldarius
Acetobacterium woodii
Clostridium aectobutylicum
Clostridium ljungdahlii
Clostridium difficile
Chlorella vulgaris
Scenedesmus obliquus
Synechococcus elongatus
Nicotiana tabacum BY-2 (plant cells)
Manual sampling-based data is often not sufficient to fully understand the bioprocess. Offline sampling is complex and time consuming, resulting in lower measurement frequency with most pulls being at the start or the end of the experiment. This means that critical information from your growth phases are being overlooked, and could have a detrimental impact on your final product. Automated online measurements, on the other hand, never miss a moment. With a high resolution growth curve, you can detect bioprocess changes in real-time.