Data Spotlight
Automated Biomass Monitoring Reduces Contamination Risks for Klebsiella pneumoniae Cultures on Antibiotic-Free Medium
Background
Carbapenems are a class of highly effective antibiotics, primarily used to treat severe bacterial infections. They are typically reserved for multidrug-resistant bacterial infections. However, multidrug-resistant gram-negative bacteria exhibit various resistance mechanisms, leading to different levels of resistance to carbapenems. In this study, mutant strains of the gram-negative bacterium Klebsiella pneumoniae were analyzed for their resistance levels and mechanisms.
Evaluating the relative cell fitness on antibiotic-free medium was crucial for characterizing the mutant strains with increased carbapenem resistance compared to the clinical isolate. The Cell Growth Quantifier (CGQ) was used to produce high-resolution growth curves. Since antibiotics could not be used—commonly applied to prevent the growth of unwanted microorganisms—it was advantageous to utilize fully automated biomass measurements instead of invasive sampling, minimizing the risk of contamination.
The detailed growth curves revealed that the two mutant strains, NRZ-33224SpMut and NRZ-33224-CRISPR-rseABC, exhibited the same growth behavior but had lower growth rates compared to the clinical isolate NRZ-33224.
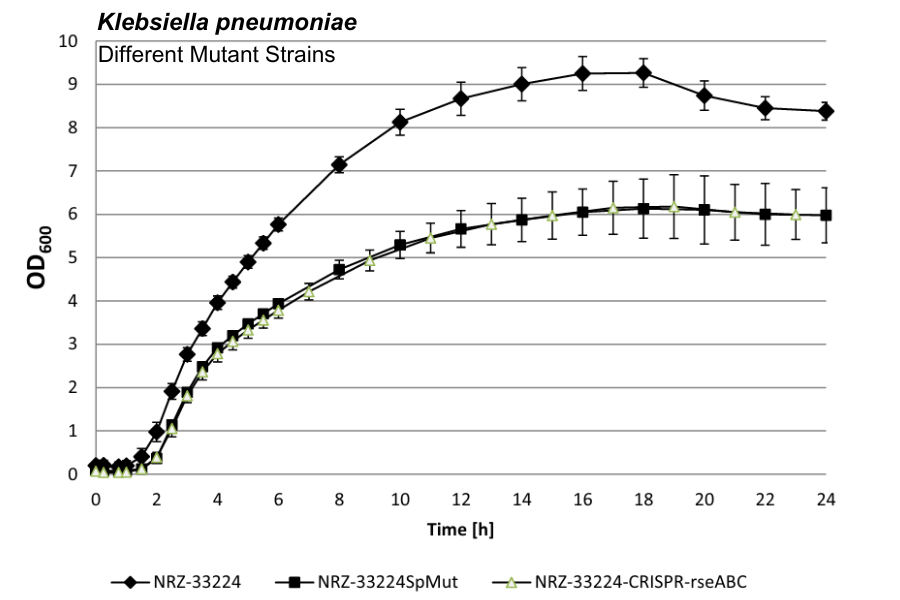
Growth profiles of three strains of Klebsiella pneumoniae, grown on antibiotic-free CAMHB medium. Shown is the average curve of triplicates with displayed error bars. Biomass was monitored with the Cell Growth Quantifier (CGQ) and backscatter values were translated to OD600 values.

Materials & Methods
Overnight cultures were inoculated in 50 mL of CAMHB to an OD600 of 0.05 +/- 0.005. Each strain was investigated in triplicates. Shake flasks were put ontop of the sensor and incubated for 24 h at 150 rpm and 37°C. The backscatter signal was translated to OD600 values for better comparability with ongoing studies.
Conclusion
Antibiotic resistance among many bacteria poses a significant health threat and is the subject of extensive research. In this study, strains of the gram-negative bacterium Klebsiella pneumoniae were analyzed for their resistance levels and mechanisms. To evaluate general cell fitness, an antibiotic-free medium was used, which increases the risk of contamination due to the potential growth of unwanted microbes. Therefore, it was crucial to minimize the risk of contamination. The fully automated biomass monitoring with the Cell Growth Quantifier (CGQ) played a key role in this effort, as it eliminated the need for manual sampling, the primary source of unwanted contamination.
Source
Cremanns et al., 2022. Effect of sigma E on carbapenem resistance in OXA-48-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae. J Antimicrob Chemother. DOI: 10.1093/jac/dkac078
Want Results Like These?
We will work with you on a solution that works best for your application.
From Estimation To High-Resolution Growth Curves
Customer Success Stories
.png)
-Kitana Manivone Kaiphanliam (Washington State University)
